ultrasound measurement of carotid artery intima-media thickness|carotid intima media thickness guidelines : member club Ultrasound measurement of carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) has become a valuable tool for detecting and monitoring progression of atherosclerosis and recently published . Em São José dos Campos. O Dan Inn São José dos Campos está localizado na Avenida João Guilhermino, 287, Centro: perto de agências bancárias, supermercados, farmácias, .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 1 de out. de 2021 · Channel Name: Globo News Channel ID: GloboNews.br Country: Brazil Language: Portuguese site: .
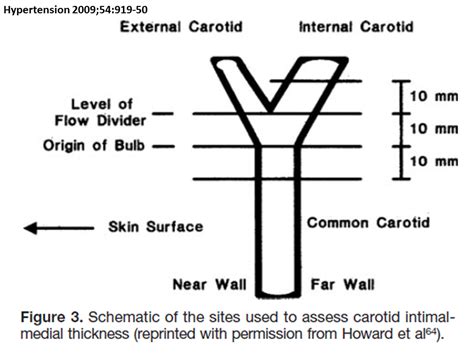
A carotid intima-media thickness test uses an ultrasound to create images of your carotid artery. Your doctor will take several measurements of your carotid arteries on . This integrative literature review assesses the use of ultrasound measured carotid artery intima-media thickness (IMT) as an early marker of CAD in adult HNC patients after .Ultrasound measurement of carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) has become a valuable tool for detecting and monitoring progression of atherosclerosis and recently published . Carotid intima‐media thickness (IMT) may be measured by ultrasound, where the distance between a double‐line reflex pattern representing the luminal‐intimal and the .
A carotid intima-media thickness test (CIMT), also known as a carotid artery IMT ultrasound scan, uses ultrasound to measure the thickness of the intima and media, the two inner layers . Automatic measurement of the intima-media thickness (IMT) from ultrasound carotid images is an important task in clinical diagnosis. Many computer-based techniques for IMT measurement have been proposed to . Ultrasound (US) measurements of carotid intima-media thickness . Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults.N Engl J Med .An in vivo evaluation of the reproducibility of intima-media thickness measurements of the carotid artery segments using B-mode ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1999;25:323–30. doi: 10.1016/s0301-5629(98)00183-5.
The carotid intima-media thickness test (CIMT) is a simple yet powerful tool for assessing heart health. This quick, painless procedure uses ultrasound to measure the thickness of the inner layers of the carotid artery walls.A CIMT . One of the most widely used and best validated atherosclerosis imaging techniques is the ultrasound carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) measurement. The techniques for imaging and measuring CIMT along with the potential clinical applications of CIMT will be discussed here. . Carotid artery imaging for the detection of significant .
normal carotid intima media thickness
Cerebrovascular accident due to carotid artery disease is the most common cause of death in developed countries following heart disease and cancer. For a reliable early detection of atherosclerosis, Intima Media Thickness (IMT) measurement and classification are important. A new method for decision .Ultrasonographic measurement of carotid intima-medial (or intimal-media) thickness (CIMT) refers to the use of B mode ultrasound to determine the thickness of the 2 innermost layers of the carotid artery wall, the intima and the media. Detection and monitoring of intima-medial thickening, which is a surrogate marker for atherosclerosis, Background and Purpose—B-mode ultrasound is a noninvasive method of examining the walls of peripheral arteries and provides measures of the intima-media thickness (IMT) at various sites (common carotid artery, bifurcation, internal carotid artery) and of plaques that may indicate early presymptomatic disease. The reported associations between . A carotid ultrasound tests for blocked or narrowed carotid arteries, which can increase the risk of stroke. The results of the test can help your health care provider determine a treatment to lower your stroke risk.
1. INTRODUCTION. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. 1 The atherosclerotic process, which causes thickening of the artery wall and reduction of the artery lumen, is the early manifestation of the possible onset of CVDs. 2,3 Studies have shown that the increase in the intima-media .Ultrasound measurement of carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and plaque thickness (PT) may be an additional tool for risk stratification of patients with suspected acute coronary syndrome (ACS) in the emergency department (ED). The aim of this study was to evaluate the correlation of CIMT and PT .
Nambi V, Chambless L, He M, et al. Common carotid artery intima-media thickness is as good as carotid intima-media thickness of all carotid artery segments in improving prediction of coronary heart disease risk in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Eur Heart J. 2012; 33:183–190. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr192.Normal values for intima-media thickness of the common carotid artery--an update following a novel risk factor profiling Vasa. 2015 Nov;44 . We evaluated IMT by high-resolution ultrasound (13 MHz) on the far wall of the common carotid artery in 801 subjects without cardiovascular disease (428 women aged 46.2±12.9 years; 373 men aged 47.3±13 .Since 2000, several guidelines suggest that carotid artery B-mode ultrasound imaging is safe, . Ultrasound protocols to measure carotid intima-media thickness in trials; comparison of reproducibility, rate of progression, and effect of intervention in subjects with familial hypercholesterolemia and subjects with mixed dyslipidemia.
Several studies suggest that carotid artery B-mode ultrasound imaging is safe, noninvasive, and relatively inexpensive. This permits an assessment of subclinical carotid atherosclerosis [20,21,22] and could improve risk stratification for cardiovascular disease (CVD) [23,24,25].In 2012, the Mannheim Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and Plaque Consensus . Common carotid artery (CCA) wall intima‐media thickness (IMT) is a noninvasive ultrasound measurement associated with cardiovascular events. 1 IMT can be measured in the CCA and in the carotid bulb/proximal . Ultrasound evaluation of carotid artery intima-media thickness (IMT) is established as a marker of carotid artery disease (CAD) and stroke risk in multiple populations, as well as a tool to evaluate the effectiveness of cardiovascular interventions (Intersocietal Accreditation Commission [IAC], 2021; Willeit et al., 2020).
The intima media thickness (IMT) has been established as an early predictor of general arteriosclerosis in patients with hypertension. However, to date, there is paucity of information on IMT of .The carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) is a widely used surrogate marker for atherosclerosis worldwide. . such as the definition of carotid plaques, the choice of measurement sites on the common or internal carotid artery, and the assessment of maximum or minimum IMT. . Other important parameters revealed by carotid ultrasound, such as .
intimal wall thickening carotid arteries
INTRODUCTION. Carotid artery intima-media thickness (CAIMT) is increasingly used as a surrogate marker of early atherosclerosis, and in a recent review it was shown that CAIMT is a strong predictor of future vascular events such as myocardial infarction and stroke.[] The normal values of CAIMT are dependent on the methodology used for its measurement, life style, food .
A third of deaths in the world are due to cardiovascular diseases [1]. Atherosclerosis is the major cause of myocardial infarction, which occurs by deposition of plaque in the coronary artery. The chance of stroke rises with the thickening of carotid artery due to the plaque. Hence, accurate measurement of the intima-media thickness is necessary for predicting the chance .
The common carotid intima–media thickness (CIMT) is measured by delineating the intima–media complex contours and is commonly used as a surrogate marker for atherosclerosis. The CIMT can be estimated via B-mode ultrasound imaging of the common carotid artery (CCA) ( Stein et al. 2008 ), and increased CIMT has been associated with .Radiopaedia.orgComparative evaluation of ultrasound measurement of carotid artery intima media thickness in hypertensive and normotensive . The B-mode ultrasound measurements of intima media thickness of the . 1. Introduction. Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) is a commonly used marker for atherosclerotic risk assessment. The CIMT is typically measured on B-mode ultrasound images of the common carotid artery (CCA) by delineating the intima-media complex (IMC) [1], although in some studies carotid Doppler images are also employed to .
A carotid intima-media thickness test (CIMT), also known as a carotid artery IMT ultrasound scan, uses ultrasound to measure the thickness of the intima and media, the two inner layers of the carotid artery.
(1998) Variance components analysis of carotid and femoral intima–media thickness measurements. REGRESS Study Group, Interuniversity Cardiology Institute of The Netherlands, Utrecht, The . Carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) is a non-invasive biomarker of atherosclerosis. . Anthropometric and blood pressure measurements were performed by standardized methods and trained medical personnel. cIMT of the right common carotid artery far wall (1 centimeter proximal to bifurcation) was determined using a multifrequency (3-13 .
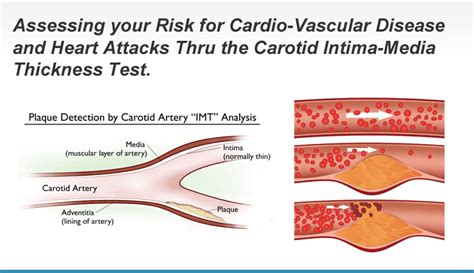
intimal thickening lower extremity ultrasound
carotid wall thickening ultrasound
web{{'CaptionDate' | translate }} {{'CaptionTicketNumber' | translate }} {{'CaptionStake' | translate }} {{'CaptionWin' | translate }} {{'CaptionStatus' | translate }}
ultrasound measurement of carotid artery intima-media thickness|carotid intima media thickness guidelines